

The table saw fit individual dice's wall frequency: Wall Number: 1 2 3 4 5 6 frequency: 8 7 5 11 6 13 Calculate the modus and median of the wall numbers that Radka fell. The age groups of the employees are: 3 employees aged 52 years, 2 aged 32 years, 1. The data set represents the number of cars in a town given a speeding ticket each day for ten days. The last value will always equal the total for all observations since the calculator will have already added all frequencies to the previous total. The cumulative frequency is calculated by adding each frequency from a frequency distribution table to the sum of its predecessors.
RANDOM MATH PROBLEM GENERATOR 7TH GRADE HOW TO
For example:į: 5 10 15 How to enter grouped data?Grouped data are formed by aggregating individual data into groups so that a frequency distribution of these groups serves as a convenient means of summarizing or analyzing the data.į: 5 10 15 How to enter data as a cumulative frequency table?Similar to a frequency table, but instead, f: write cf: in the second line. Each element must have a defined frequency that counts numbers before and after symbol f: must be equal. Write data elements (separated by spaces or commas, etc.), then write f: and further write the frequency of each data item. Multiplying Fractions by Whole Numbers e.g.How to enter data as a frequency table?Simple.Fraction of a Whole Number (From Worksheet).
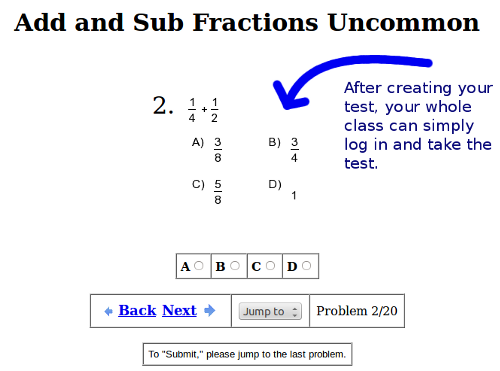

Similar to the above listing, the resources below are aligned to related standards in the Common Core For Mathematics that together support the following learning outcome:īuild fractions from unit fractions by applying and extending previous understandings of operations on whole numbers
Subtracting Mixed Numbers (same denominator) e.g.Subtracting Fractions (same denominator e.g.Adding Mixed Numbers (same denominator) e.g.Adding Fractions (same denominator) e.g.Blank – Marked at the Ninths (with option of 1 to 8 lines/ page).Blank – Marked at the Eighths (with option of 1 to 8 lines/ page).Blank – Marked at the Sevenths (with option of 1 to 8 lines/ page).Blank – Marked at the Sixths (with option of 1 to 8 lines/ page).Blank – Marked at the Fourths (with option of 1 to 8 lines/ page).Blank – Marked at the Thirds (with option of 1 to 8 lines/ page).Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole and having like denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem.Add and subtract mixed numbers with like denominators, e.g., by replacing each mixed number with an equivalent fraction, and/or by using properties of operations and the relationship between addition and subtraction.Justify decompositions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model. Decompose a fraction into a sum of fractions with the same denominator in more than one way, recording each decomposition by an equation.Understand addition and subtraction of fractions as joining and separating parts referring to the same whole.Understand a fraction a/b with a > 1 as a sum of fractions 1/b. The various resources listed below are aligned to the same standard, (4NF03) taken from the CCSM ( Common Core Standards For Mathematics) as the Fractions Worksheet shown above.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
